An aerobic organism or aerobe is an organism that can survive and grow in an oxygenated environment.
Types
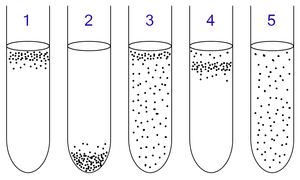
- Obligate aerobes need oxygen to grow. In a process known as cellular respiration, these organisms use oxygen to oxidize substrates (for example sugars and fats) and generate energy.
- Facultative anaerobes use oxygen if it is available, but also have anaerobic methods of energy production.
- Microaerophiles require oxygen for energy production, but are harmed by atmospheric concentrations of oxygen (21% O2).
- Aerotolerant anaerobes do not use oxygen but are not harmed by it.
Glucose>

A good example would be the oxidation of glucose (a monosaccharide) in aerobic respiration.
- C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 38 ADP + 38 phosphate â†' 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + 38 ATP
Oxygen is used during the oxidation of glucose and water is produced.
This equation is a summary of what actually happens in three series of biochemical reactions: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
See also

- Aerobic digestion
- Anaerobic digestion
- Facultative anaerobic organism
- Fermentation (biochemistry)
- Microaerophile
- Obligate anaerobe



0 komentar :
Posting Komentar